

Copyright©IBMI & RBMP. All contents in this study are copyrighted. Please cite sources with a link back to this study if you wish to share the contents.
The following study was conducted by the Institute for Biotechnology and Medicine Industry (IBMI) and the Research Center for Biotechnology and Medicine Policy (RBMP), drawn from five facets:
1. EUA Status of Global COVID-19 Vaccines;
2. Global Vaccine Research Progress and Platforms Used;
3. Analysis of Vaccine Development by Country;
4. COVID-19 Vaccine Developers and Champions, and
5. Countries Dominating COVID-19 Vaccine Manufacturing.
Since the coronavirus outbroke in January, 2020, Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) has been granted for 20 vaccines in 18 months. That includes 7 vaccines developed in China, 4 in Russia, 3 in US (one of which partnered with Germany), 2 in Iran (one of which partnered with Cuba), and one each from UK, India, Kazakhstan, and Cuba.
Amongst 20 vaccines, only 6 had nevertheless been added to the Emergency Use Listing (EUL) by WHO at the end of June: Pfizer-BioNTech (US-Germany), J&J/Janssen (US), Moderna (US), Oxford-AstraZeneca (UK), Sinopharm-BBIBP and CoronaVac (China), with the previous four connected to the EU Digital COVID Certificate (EDUCC). Please be advised that AZ/SKBio, AZ/EU, and Covishield (AZ vaccine produced in India) are regarded as one AZ vaccine, hence the exclusion.
Table 1. List of COVID-19 Vaccines with EUA
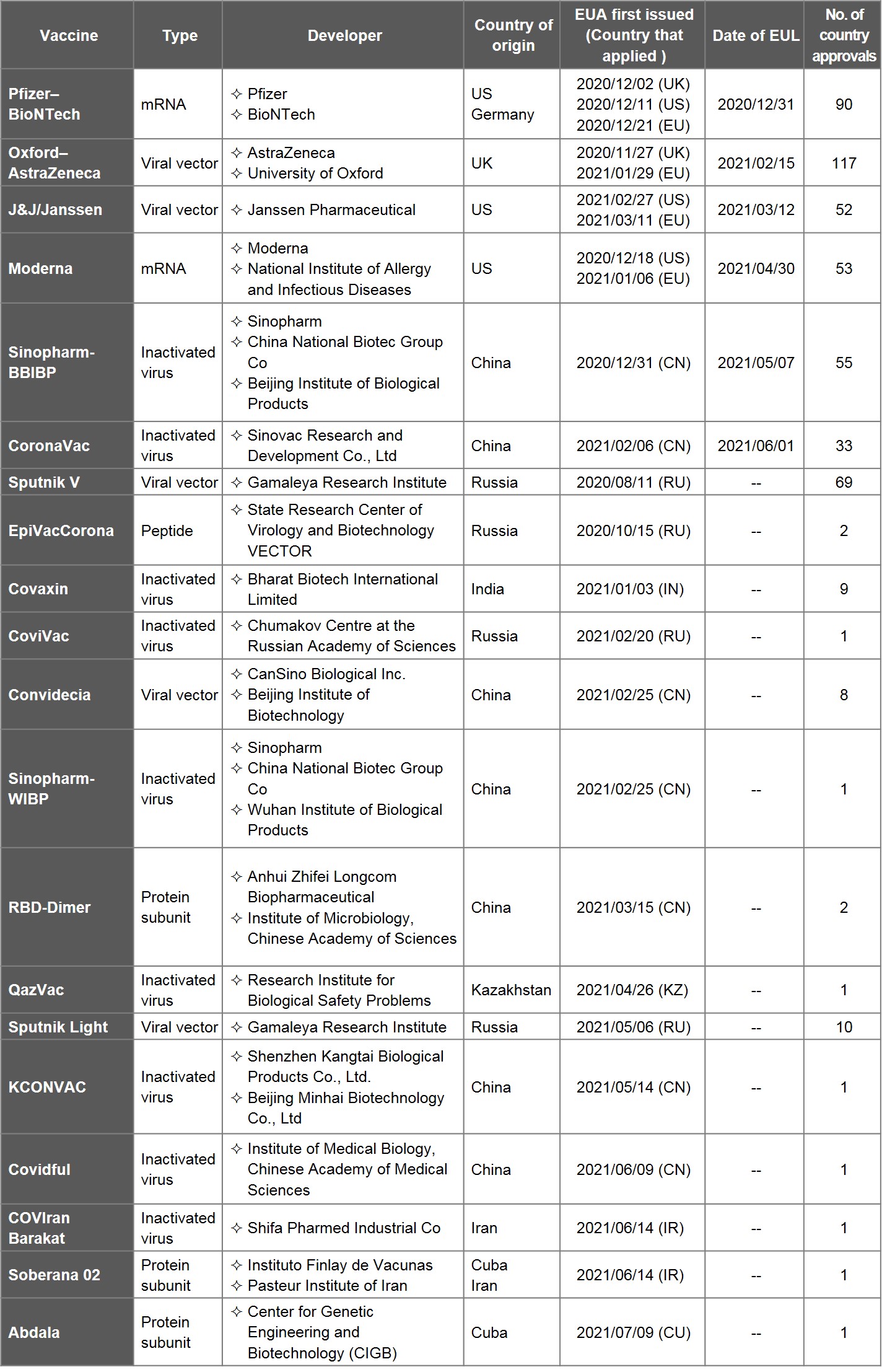
Source: data and information collected from WHO, health authorities and media outlets, compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
Note:
1) Cuba has begun administering large numbers of its own Soberana 02 and Abdala vaccines since 14 May. The Abdala vaccine has received EUA, while the Soberana 02 vaccine is still under review by CECMED, the local regulatory body.
2) EUA-listed vaccines will be updated on a rolling basis.
As per WHO's "COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape" as of 30 June, 2021, 287 vaccines worldwide have been in the pipeline. In addition to 6 EUL-listed vaccines, there are 97 ones undergoing clinical trials- including 25 in phase III and phase II/III, 37 in phase II and phase I/II, and 35 in phase I. The other 184 vaccines are doing preclinical studies.
Nucleic acid, viral vector and whole virus are technology platforms that 6 EUL vaccines employed, two by each. In terms of main approaches to designing a vaccine, 36.2% of vaccines opted for protein subunit- 9 of which have entered phase III and phase II/III, including the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine by the US-based Novavax, and VAT00002 developed by Sanofi and GSK; 23% proceeded with nucleic acid, including the vaccine by CureVac of Germany, followed by 21.3% with viral vector, 8% with virus-like particles (VLP) and 10.1% with whole virus.
In terms of dosage forms, over 90% of vaccines are injections. Most recently countries have also begun development of inhalation or oral dosage forms. Convidecia by CanSino Biologics (China), which has been approved the use of injection, is now under EUA review for a form of nasal spray. Meanwhile, Wantai Biological (China) has completed phase II of its intranasal vaccine.
Table 2. Overview of Global Vaccine Research Progress and Vaccine Platform
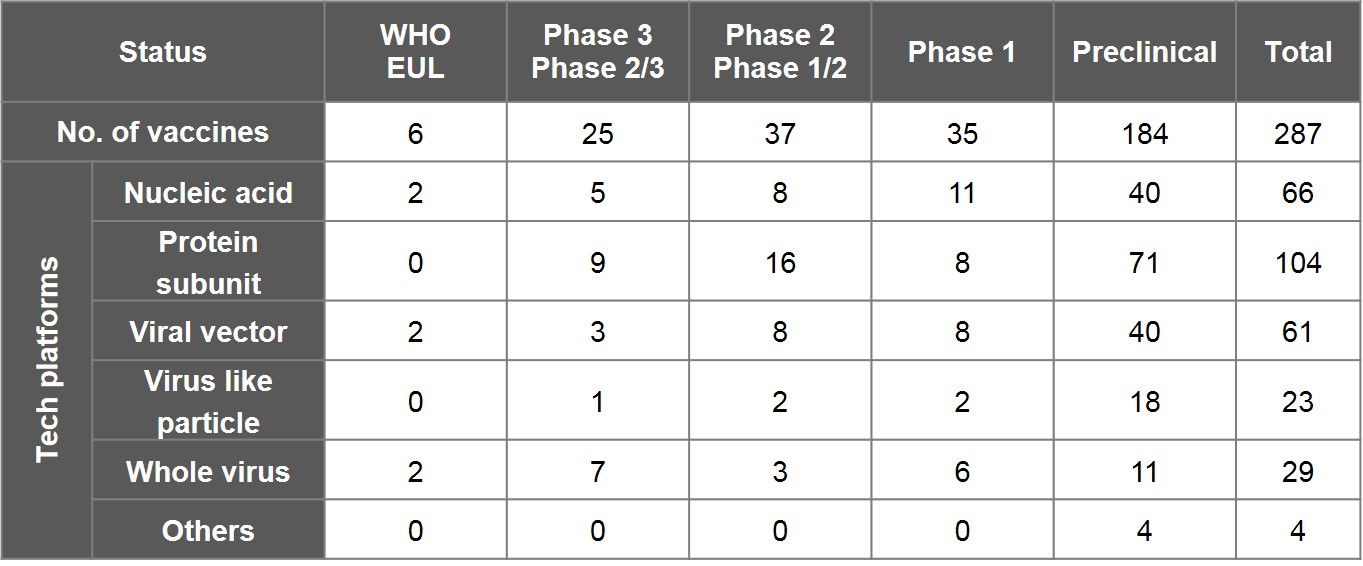
Note:
1) As the aforementioned datasets were collected and compiled by the WHO R&D Blueprint team and also include data submitted by various institutions, there may be omissions and inconsistency between time logged and actual progress. Certain vaccines in development had terminated, such as the monoglycosylated S-protein subunit universal vaccine and mRNA vaccine led by the president of Academia Sinica, and the DNA vaccine by Taiwan's National Health Research Institute and Enimmune. Table 2 excludes Sputnik Light and CoviVac by Russia but includes research projects such as Medigen's MVC-COV1901, United BioPharma's UB-612 (Vaxxinity), and Adimmune's AdimrSC-2f.
2) The numbers shown underneath phase III or phase II/III include 11 vaccines that have been authorised emergency use by certain countries despite exclusion from EUL: Russia's Sutnik V (Gamaleya) and EpiVacCoronoa (FBRI), India's Covaxin (Bharat Biotech), China's Convidecia (CanSino Biologics), RBD-Dimer (Zhifei Longcom), Covidful (Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences), Sinopharm-WIBP (Sinopharm), and KCONVAC (Kongtai Biological Products), Kazakhstan's QazCovid-in® (Kazakhstan RIBSP), Iran's COVIran Barekat (Shifa), and Cuba's Abdala (CIGB).
3) Technology platforms here are inclusive of DNA and RNA vaccines by nucleic acid; peptide vaccines by protein subunit; inactivated vaccines and attenuated vaccines by whole virus; and bacterial vector and cell-based vaccines categorised as “Others”.
Figure 1. Global Vaccine Research Progress by Platform
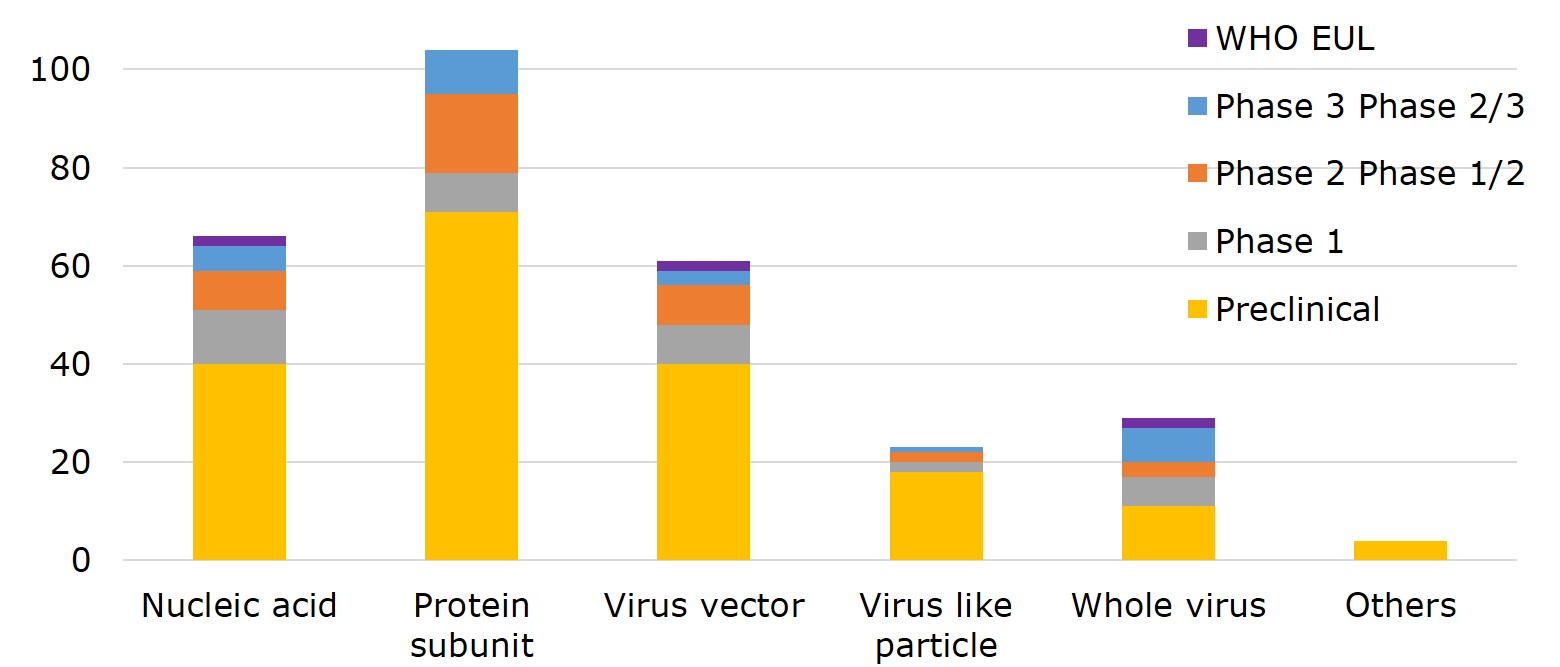
Source: WHO, compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
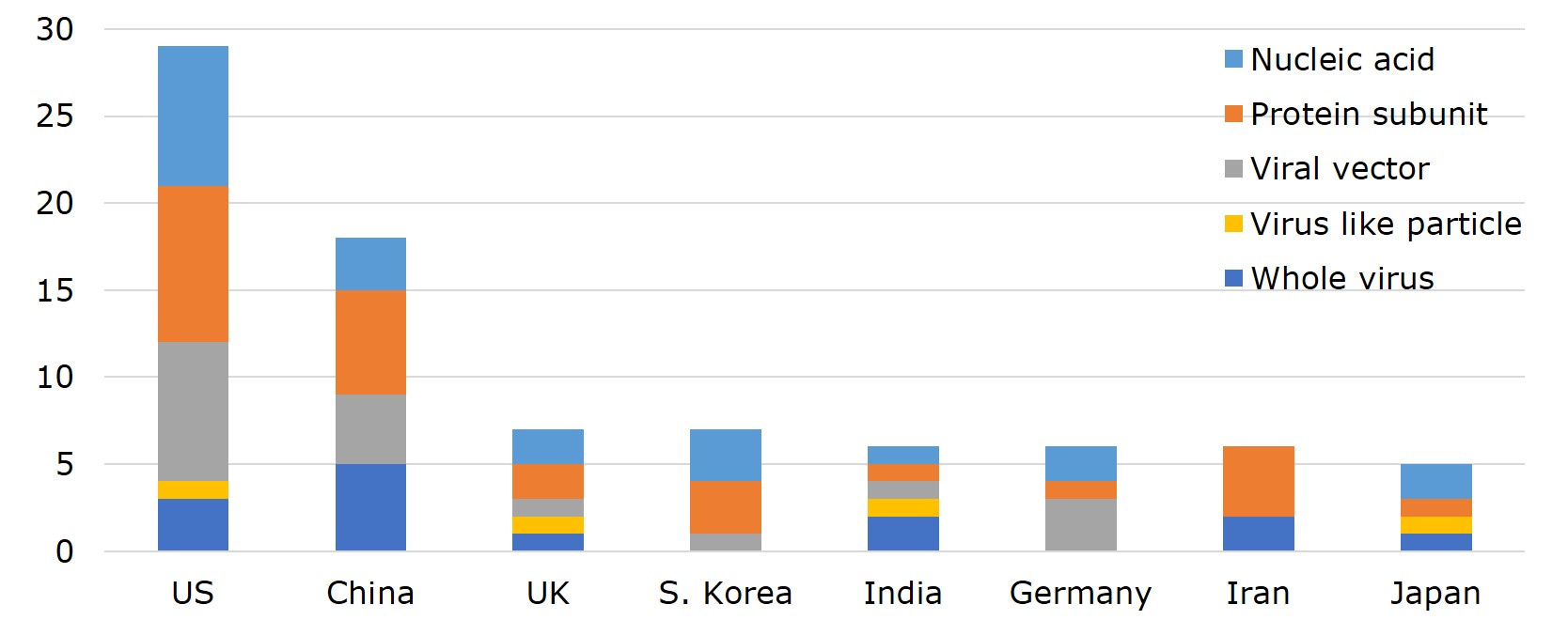
According to WHO, vaccines developed by 25 different countries globally have entered clinical trials. Ranking the countries by the number of vaccines with EUA and that of clinical trials, US leads with 29 vaccines in clinical trials, 3 of which made to EUL and 3 in phase III. Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna have already filed for Biologics License Application (BLA) with FDA. Currently, the vaccine-making tech platforms most adopted by US companies are nucleic acid (DNA&RNA), viral vector, and protein subunit. Vaccine developers- Moderna, Pfizer, Novavax and J&J, were funded under the Operation Warp Speed programme initiated by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), with $4.1bn, $1.95bn, $1.6 bn, and $1.45 bn, respectively. The funding was for R&D, manufacturing and procurement.
China ranks second to the US with 18 vaccines- 7 of which have been approved for use either in China or elsewhere, including 2 listed by EUL. In China, the primary vaccine platforms used are whole virus, protein subunit, and viral vectors. The UK and South Korea each have 7 vaccines on the list. However, UK already has one vaccine on EUL, 3 in phase III or phase II/III trials, whereas all 7 of South Korea's vaccines are still in early phase I or phase II. Germany, India, and Iran each has 6 vaccines in development. Germany adopts mainly nucleic acid and viral vector as the platform of choice, has 1 vaccine on EUL, while 2 more are in late-stage trials. Japan also has 5 vaccines in the pipeline, with 2 (nucleic acid and virus-like particle) in phase III.
Figure 2. Number and Development Stage of Vaccines in Clinical Trial across 25 Countries
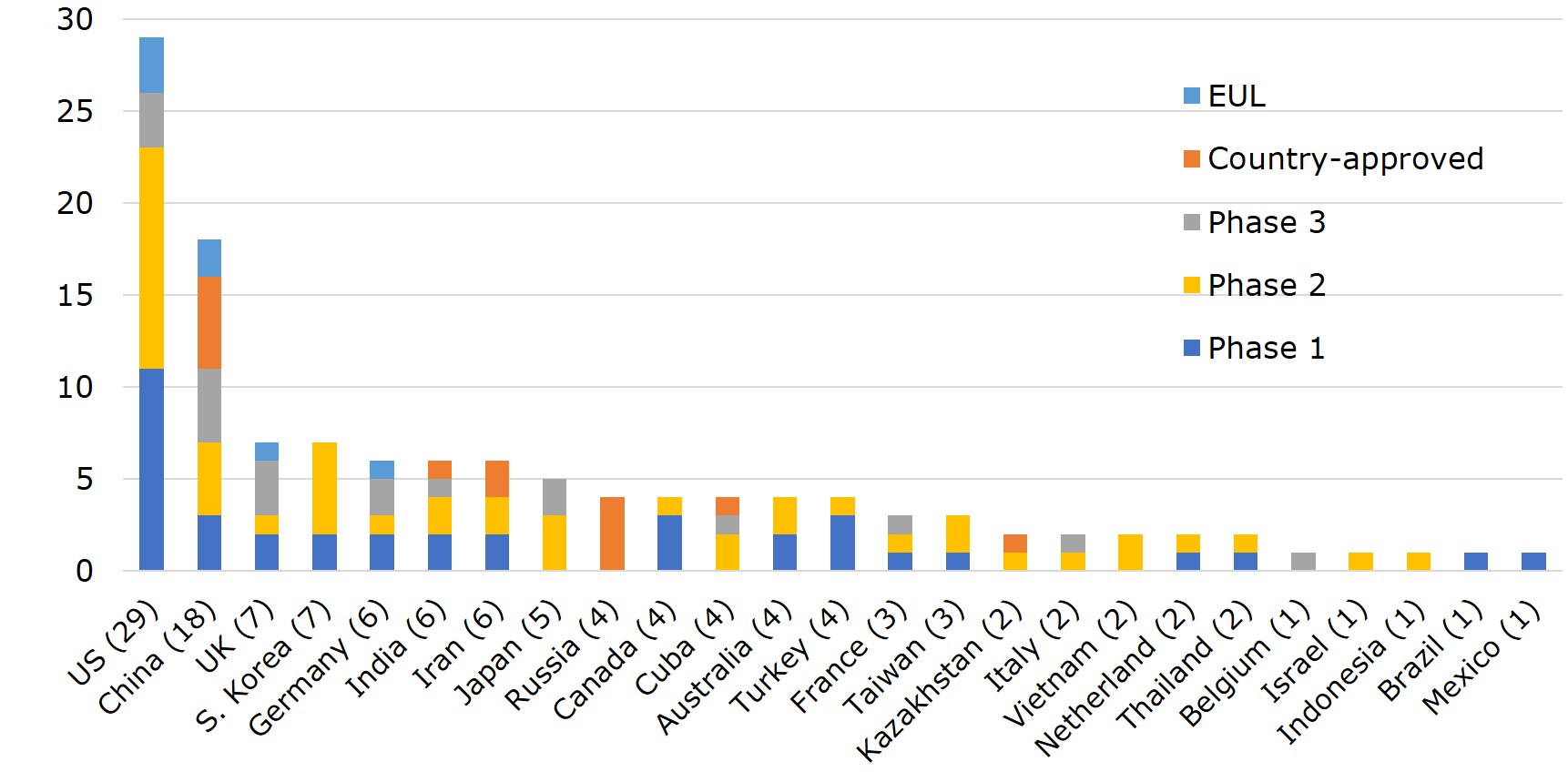
Source: WHO; compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
Note:
1) For co-developed vaccines, countries that involved were counted one each.
2) Vaccines developed in Taiwan: Medigen's MVC-COV1901 (phase II), United BioPharma's UB-612 (phase II), and Adimmune's AdimrSC-2f (phase I).
Figure 3. Leading Countries by Platform and Development Stage
Source: WHO; compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
Analysing 20 vaccines with EUA, there are 23 entities that participated and succeeded in developing vaccines. Amongst this cohort, 12 refer to companies, 12 refer to universities and research institutes.
Viewed by capital values of companies between $103m and $65.5bn, Shenzhen Kangtai Biological is the smallest, Pfizer is the largest. The number of employees ranges between 500 to 96,500. The youngest company is Moderna, an emerging biotechnology company in the US founded in 2010. Of the 12 companies, 8 are publicly traded, while 4 either have not been traded publicly or have had their trading suspended. The market values of the publicly traded companies range between Pfizer's $218.4bn and Sinopharm Group's $9.31bn. Companies whose market value have changed most significantly since beginning vaccine research are Moderna, BioNTech, and China's CanSino Biologics, which have grown 16 times, 13.4 times, and 6.9 times, respectively, between 31 October 2020 and 30 June 2021. Companies that shrunk in market value also exist, an example being China's Sinopharm Group.
Table 3. List of Leading Developers of Vaccine Development
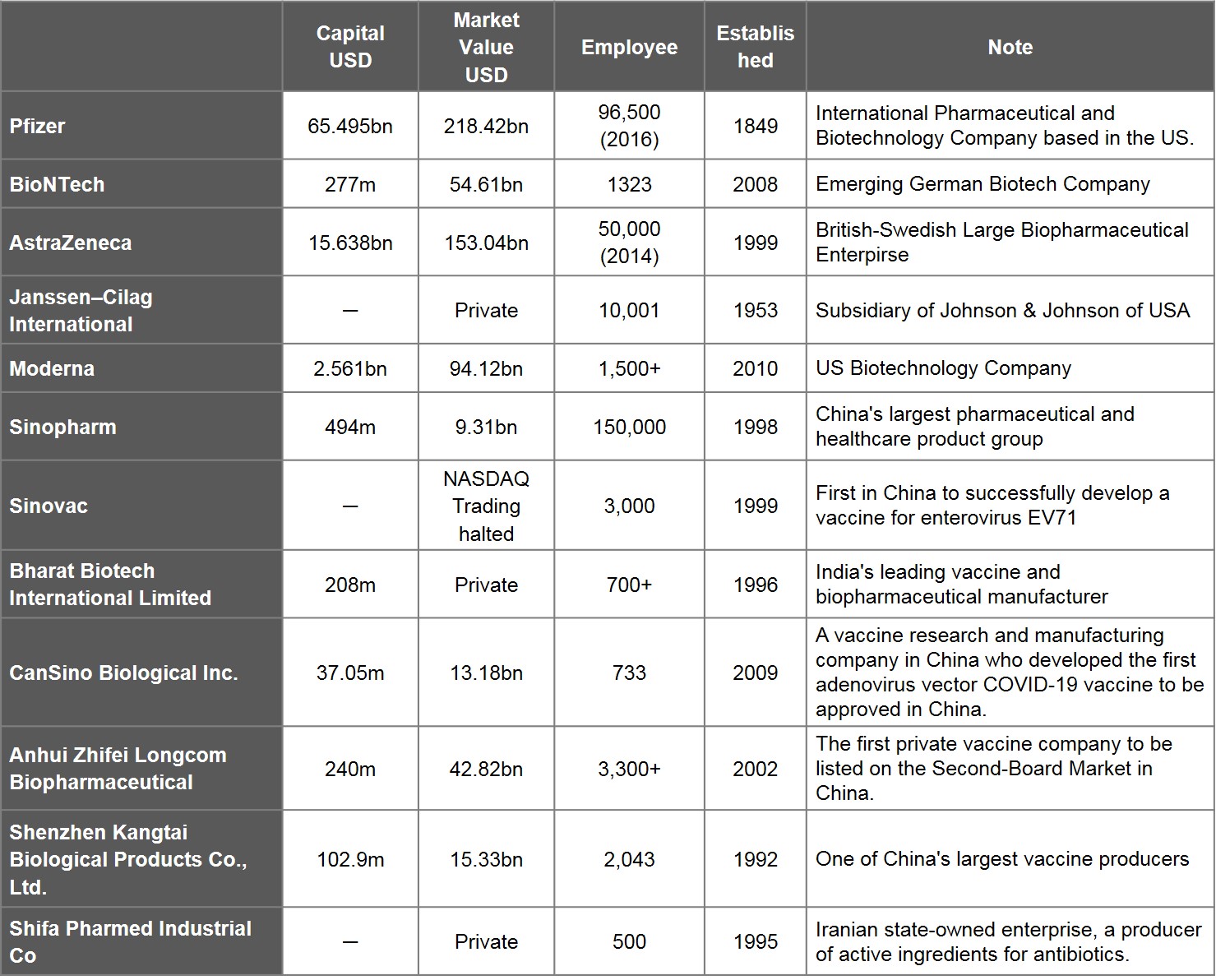
Source: WHO and publicly available information on companies, stock exchanges and finances; compiled by IBMI & RBMP. Market value of companies as of 30 June, 2021.
Note: If the companies participating in vaccine development are part of the same group or parent-child companies, they are counted as one. E.g. China National Biotec Group Co., Beijing Institute of Biological, and Wuhan Institute of Biological Products are all part of the Sinopharm Group, while Beijing Minhai Biotechnology Co., Ltd. is a subsidiary of Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products Co., Ltd.
Figure 4. Market Value Trends of Leading Vaccine Developers
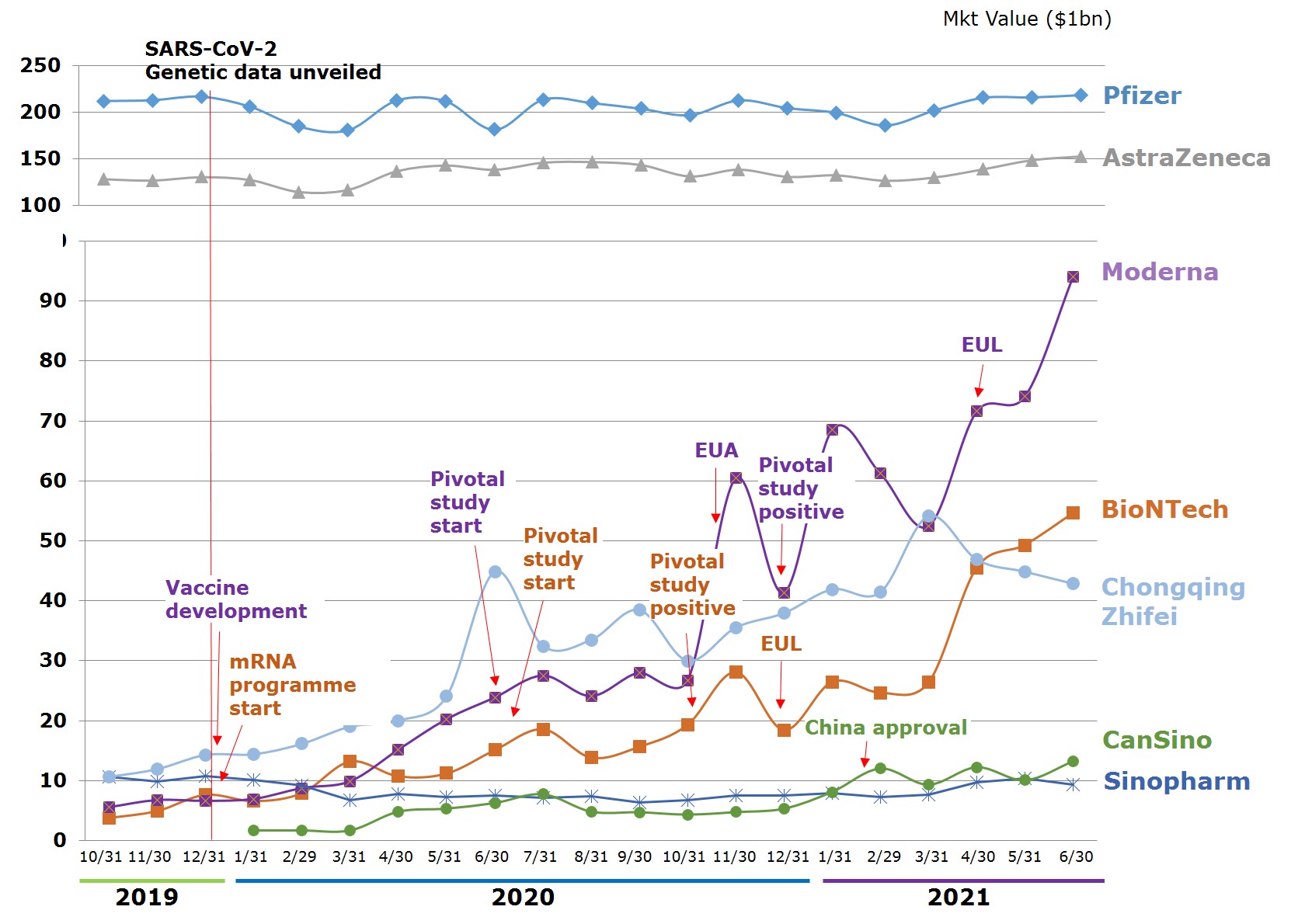
Source: Publicly available information on companies and data released by stock market exchange; compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
Of the remaining organisations, Oxford University is the lone school while the other 11 are all research institutes under government agencies. Six of the said institutes are vaccine research centres: Institute of Bioengineering of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences of China, Russia's Gamaleya Research Institute, VECTOR, and Chumakov Centre at the Russian Academy of Sciences, Kazakhstan's Research Institute for Biological Safety Problems, and Cuba's Finlay Vaccine Institute.
Table 4. List of Leading Research Institutes for Vaccine Development
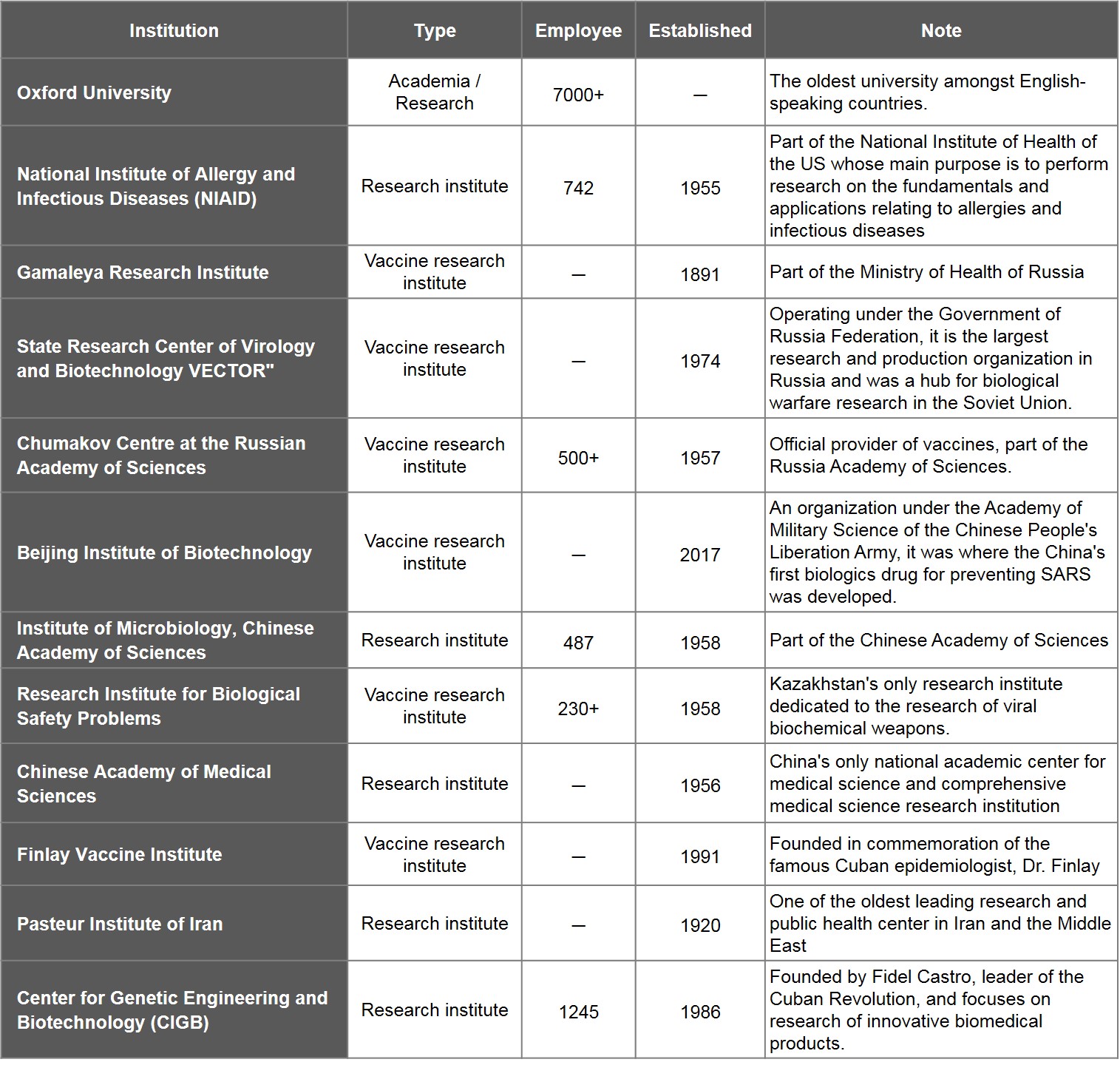
Source: WHO, medica outlets and publicly available information of research institutes; compiled by IBMI & RBMP.
To understand the distribution of leading countries producing vaccines, the study analysed the 6 prominent vaccines, i.e., EUL vaccines. Currently, 6 EUL vaccines are produced by 44 companies. US is home to the highest number of manufacturers, with 10 on its soil, followed by Germany with 5, Japan with 4, and China, Belgium, and the Netherlands with 3 each.
Vaccine manufacturing can be split into two major stages: drug substance and drug product, which can be manufactured separately at different factories. In general, the technology involved in the production of the drug substances is more complex and represents a higher barrier to entry. In particular, the production of mRNA vaccines is the most challenging. The main procedures of the process include extracting viral DNA and placing it in a microbe, fermentation of the microbe, DNA purification, DNA transcription, mRNA purification, and encapsulation by lipid-nano particles. Generally speaking, the production of drug substances is done in the country where the vaccine is originated, including 6 in US, 4 in Germany, and 3 in China. A few of nations capable of making mRNA vaccines are Germany, US, and Switzerland.
Table 5. Global Manufacturers of 6 EUL Vaccines
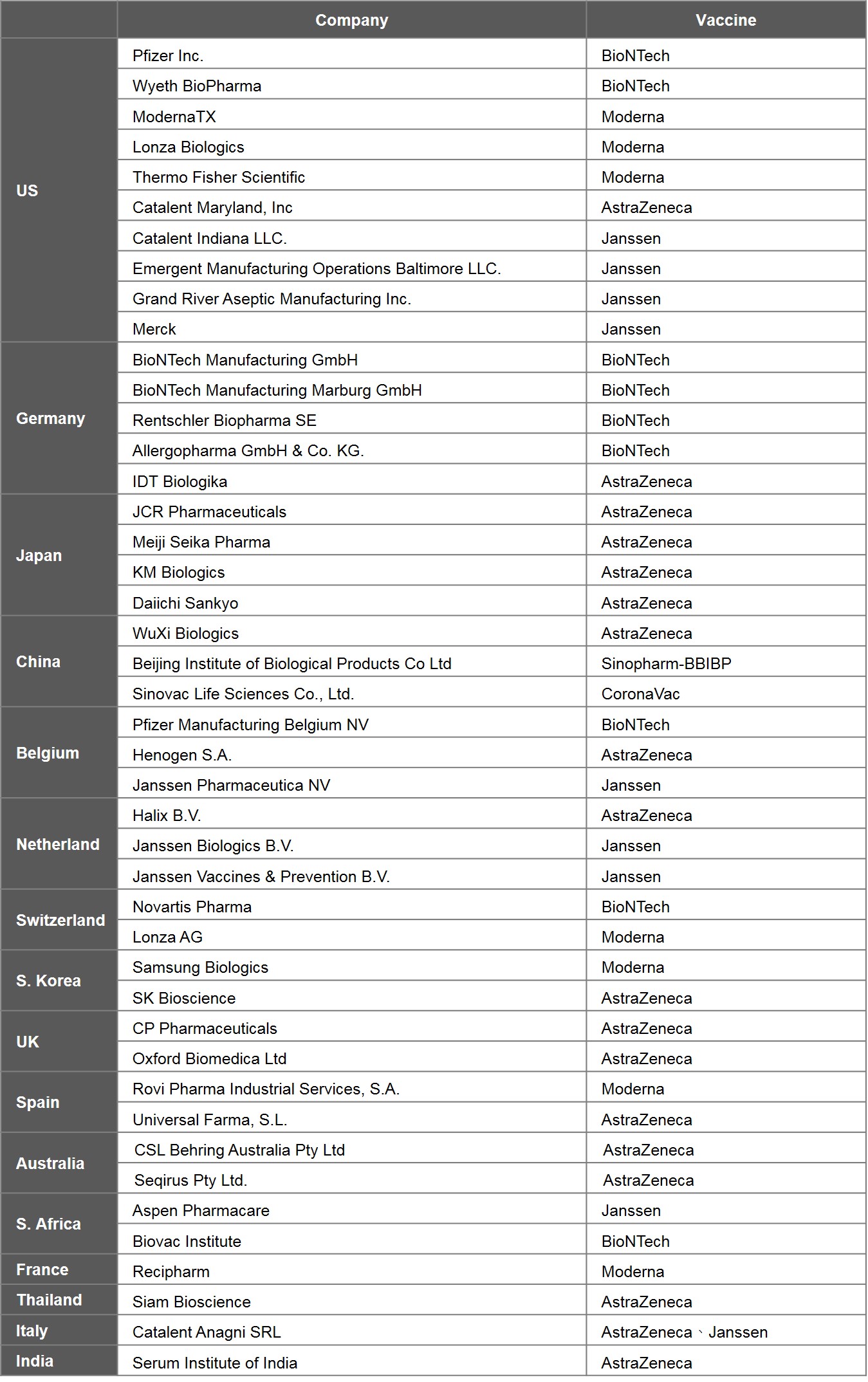
Source: EMA, WHO and publicly available information on companies hereby listed.
Note:
1) The production plants of Pfizer based in US are located in Kalamazoo, Michigan; Andover, Massachusetts; Chesterfield, Missouri; Groton, Connecticut; and McPherson, Kansas. Each plant involved in a different stage of vaccine manufacturing.
2) The above information may not be the latest by the time this study went online, which will be updated on a rolling basis.
Figure 5. Drug Substance Manufacturers of 6 EUL Vaccines by Country
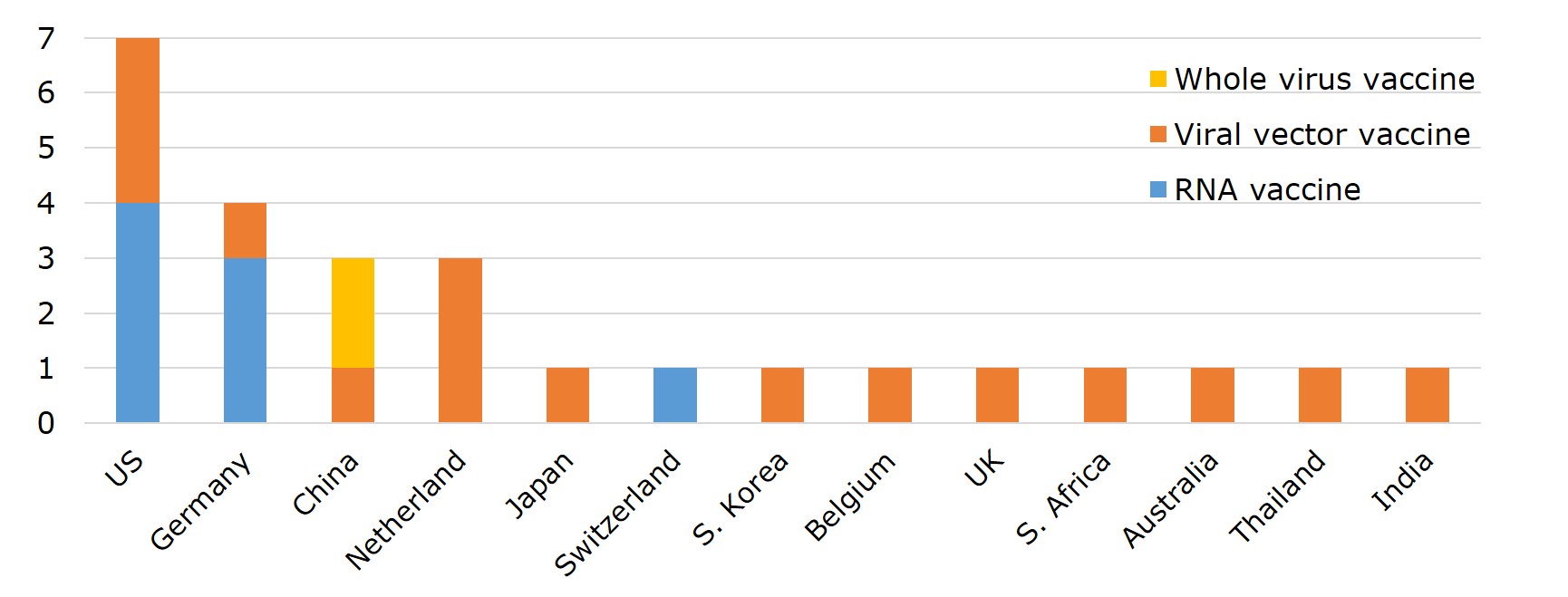
Source: EMA, WHO and publicly available information on companies hereby listed.
Copyright © IBMI & RBMP. All contents in this study are copyrighted. Please cite sources with a link back to this study if you wish to share the contents.

